Best Kidney Biopsy Hospital In Vijayawada
What is Renal Biopsy?
A renal biopsy, also known as a kidney biopsy, is a medical procedure in which a small piece of kidney tissue is removed for laboratory examination. This test helps doctors determine the underlying cause of kidney problems, monitor the progression of kidney disease, or evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Under the care of Dr. M.V. Viswanath, an experienced nephrologist, Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre offers expert-guided renal biopsies using the latest techniques for precise diagnosis and safe outcomes. If you're searching for the best Kidney Biopsy Treatment Doctor in Vijayawada, Dr. M.V. Viswanath is a trusted name in the field.
Why is a Renal Biopsy Performed?
A renal biopsy is typically recommended when there are unexplained abnormalities in kidney function, such as:
- Blood or protein in the urine (hematuria or proteinuria)
- Declining kidney function with no clear cause
- Persistent swelling or fluid retention
- Suspected kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis)
- Monitoring of kidney transplant rejection or disease recurrence
It allows the physician to observe the structure of the kidney tissue under a microscope to identify the specific cause of the disease.
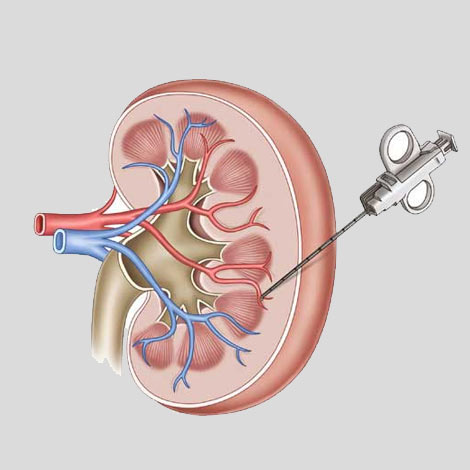
How is the Kidney Biopsy Procedure Done?
Renal biopsy is usually performed under local anesthesia and ultrasound or CT scan guidance. The most common type is the percutaneous kidney biopsy, which involves the insertion of a special biopsy needle through the skin into the kidney.
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-procedure blood tests to evaluate clotting and kidney function
- Use of imaging to locate the kidney
- Application of local anesthesia
- Insertion of the needle to retrieve a small tissue sample
- Pressure applied to the area after the sample is taken to prevent bleeding
The entire procedure usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes. Afterward, the patient is monitored for several hours to rule out complications.
Risks and Complications of Renal Biopsy
While kidney biopsy is generally a safe procedure, some potential risks may include:
- Bleeding at the biopsy site
- Infection
- Pain or discomfort in the lower back or side
- Blood in the urine (usually temporary)
- Rare risk of injury to surrounding organs
At Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre, safety is prioritized. Each biopsy is performed under sterile conditions with real-time imaging to ensure precision and minimize risk.
What to Expect After the Procedure
After the biopsy, patients are generally advised to rest in bed for 4 to 6 hours and avoid strenuous activity for at least 1 to 2 weeks. It is common to experience mild discomfort or blood in the urine for a day or two. If you experience prolonged bleeding, fever, or severe pain, it's essential to contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Benefits of Renal Biopsy
Renal biopsy offers valuable insights that help physicians:
- Accurately diagnose the type and extent of kidney disease
- Determine the best treatment strategy
- Predict disease progression and prognosis
- Assess response to treatment in existing kidney disorders
This diagnostic tool plays a crucial role in customizing care plans, especially for patients with complex or chronic kidney conditions.
Who Should Perform a Renal Biopsy?
A renal biopsy should only be performed by a trained nephrologist or interventional radiologist. Dr. M.V. Viswanath at Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre is highly experienced in performing kidney biopsies with utmost precision and care. If you are looking for a reliable Kidney Biopsy Treatment Hospital in Vijayawada, this center offers advanced facilities and personalized care.
How to Prepare for a Kidney Biopsy
Before undergoing a kidney biopsy, patients may be advised to:
- Stop taking blood-thinning medications (like aspirin or warfarin)
- Undergo blood tests to assess bleeding risk
- Fast for a few hours before the procedure, if recommended
- Inform the doctor about allergies or medical conditions
Following pre-procedure instructions is essential for a smooth and safe biopsy experience.
Why Choose Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre?
Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre is a leading nephrology facility offering comprehensive kidney care in Vijayawada. Under the guidance of Dr. M.V. Viswanath, the hospital provides high-precision diagnostics and treatments for various renal disorders. Known as a trusted Kidney Biopsy Treatment Doctor in Vijayawada, Dr. Viswanath combines experience, technology, and patient-centered care.
The hospital’s commitment to quality, safety, and innovation makes it a preferred destination for patients seeking Kidney Biopsy Treatment Hospital in Vijayawada.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the purpose of a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy helps diagnose the cause of abnormal kidney function, monitor disease progression, and guide treatment decisions. -
Is a kidney biopsy painful?
Most patients feel only mild discomfort. Local anesthesia is used to numb the area, making the procedure relatively painless. -
How long does recovery take?
Most patients can resume light activities within 24–48 hours, but strenuous activities should be avoided for a week or more. -
Will I need to stay in the hospital?
In most cases, renal biopsy is done as an outpatient procedure, but a short hospital stay may be required for observation in some cases. -
Are there any side effects after the biopsy?
Minor side effects may include mild pain and temporary blood in the urine. Serious complications are rare. -
Can a kidney biopsy detect cancer?
Yes, a renal biopsy can help detect kidney tumors or cancerous growths by examining tissue structure under a microscope. -
Who is not suitable for a renal biopsy?
Patients with bleeding disorders, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or a single kidney may not be suitable candidates for this procedure. -
How accurate is a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy provides high diagnostic accuracy when performed correctly and interpreted by expert pathologists. -
Why choose Dr. M.V. Viswanath for my renal biopsy?
Dr. M.V. Viswanath is a skilled and experienced nephrologist known for safe, accurate, and patient-focused kidney biopsy procedures in Vijayawada.
A renal biopsy is a crucial diagnostic procedure in nephrology, offering deep insights into kidney health. At Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre, patients receive advanced and compassionate care under the supervision of Dr. M.V. Viswanath, a leading Kidney Biopsy Treatment Doctor in Vijayawada.
If you're experiencing signs of kidney disease or have been advised to undergo a renal biopsy, trust the expertise of Veda Hospital & Kidney Centre, recognized as a premier Kidney Biopsy Treatment Hospital in Vijayawada.
Best healthcare providers

Unmatched Nursing Support

Top-notch Patient Care

Hospitable environment

Phenomenal intervention